Image Recognition
Product Setup Requirements
What information is required for SKU setup?
- Minimum 5 Megapixel images of product packaging from all angles
- For cylindrical products:
- 3-4 images around the circumference
- 1-2 images from the top
- Complete packaging information including branding and color for visual representation
Planogram Management
How many planograms are typically needed?
A market usually requires only a small number of planograms. These are defined based on combinations of:
- Market
- Channel
- Classification
- Equipment type
For example, a single market might have different planograms for:
- Highway-adjacent stores
- City center locations
What information is needed for planogram setup?
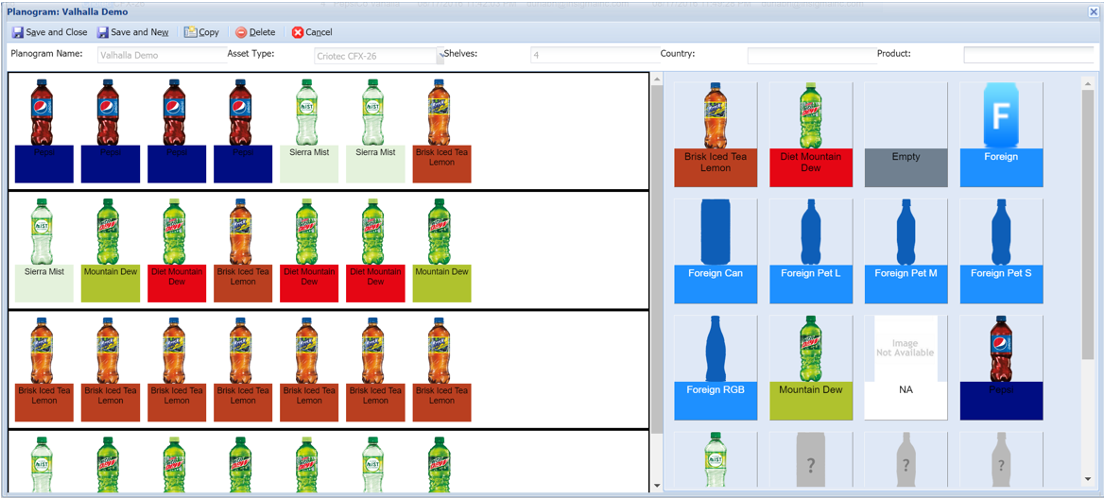
To create a planogram, you need:
- Complete product setup
- Shelf specifications
- Asset type details (if planogram is specific to certain cooler/freezer models)
Who can manage planograms?
Any user with planogram modification privileges can:
- Create new planograms
- Assign planograms to assets
Priorogram System
What is a priorogram?
Priorogram is Coolr's proprietary approach to handling "missed opportunities" and "order recommendations" for out-of-stock situations. This system was developed to address common challenges with traditional planograms:
- Traditional planograms can be tedious to set up
- Field implementation often deviates from defined planograms due to practical constraints
The priorogram model allows customers to:
- Specify SKUs in order of priority
- Focus on product availability rather than specific positioning
- Receive recommendations based on priority list and current inventory
Stock Calculation Methods
How is stock calculated across different tiers?
Basic Tier/Navigator
- Uses Share of Shelf (SoS) or Share of Visible Inventory (SOVI)
- Common approach among traditional image-based monitoring solutions
Commander and Pioneer Tiers
- Utilizes depth estimation for stock calculation
- Stock levels are approximated in 25% increments (25%, 50%, 75%, 100%)
- Camera positioning affects measurement:
- Horizontal freezers: Top-mounted camera provides accurate stock level assessment
- Vertical freezers: Front-mounted camera measures stock by product distance from shelf front
How accurate is stock calculation?
- Approximately 95% accurate across 30,000+ units
- Successfully used for order recommendations across various businesses
- Proven track record of 30%+ sales uplift in first year when recommendations are followed
Can exact stock counts be obtained?
While Coolr's solution prioritizes cost-effectiveness and quick ROI with 95%+ accuracy, alternative solutions for exact counting include:
- Grab 'n Go systems
- Just Check Out
- Weight sensors
- RFID technology
Key Metrics and Calculations
What are the key performance metrics?
Stock (SOVI - Share of Visible Inventory)
- Used to identify:
- Replenishment schedules
- Product sale patterns at SKU level
Planogram/Priorogram Compliance
- Measures:
- Product portfolio effectiveness
- SKU-level placement efficiency
- Out-of-stock situations
- Product distribution
Purity
- Measures percentage of customer's own products in an asset
- Also known as Share of "own" inventory
- Used for trade terms compliance monitoring
How are metrics calculated?
Standard calculations include:
Stock % = (Total Visible Products - Foreign Products) / Total Available Positions
Purity = (Total Visible Products - Foreign Products) / Total Visible Products
Planogram Compliance = (Total Planogram Facings - Compliant Facings) / Total Available Positions
Note: Total Available Positions is determined by either:
- Defined planogram occupied spaces
- Or (Shelves × Columns per shelf) as specified in Asset Type configuration
Image Recognition Process
What is Coolr's image recognition workflow?
-
Image Processing
- Stitching of fragmented images
- Human feature obfuscation
- Area of interest cropping
- Perspective correction (fish-eye reduction)
- Quality adjustment (brightness, contrast)
-
Detection Steps
- Shelf/basket identification
- Product shape detection
- Empty space recognition
- SKU identification
- Stacking analysis
- Stock level assessment
What is the accuracy level and how is it maintained?
- 95%+ accuracy in automated recognition
- Verification process:
- Random 20% of images undergo human review
- Minimum 10 SKUs per test set
- Regular benchmarking across 1,000 images
- Diverse location/asset sampling
Why is continuous training necessary?
Image recognition, like human learning, requires ongoing training to handle:
- Seasonal packaging changes
- New product variants
- Similar product differentiation
- Image quality variations
- Product placement variations
The system must continuously learn to:
- Distinguish between similar products
- Recognize new packaging designs
- Adapt to different viewing angles
- Handle varying light conditions
- Process multiple product variations
Business Applications
What are the key use cases for this data?
- Inventory optimization
- Improved on-shelf availability
- Portfolio optimization
- Merchandising management
- Standards monitoring and enforcement
- Cost and carbon footprint reduction
- Compliance
- Trade terms enforcement
- Unbiased continuous monitoring
- Business optimization
- Missed opportunity identification
- Delivery routing optimization